Have you ever wondered why certain economies seem to promote societal equity more effectively than others? Imagine a scenario where one city has a relatively equal income distribution among its residents, as opposed to another city where wealth is highly concentrated in the hands of a single individual.
The concept giniä seeks to quantify that difference, a value that indicates the level of income disparity within a given population. In this article, we will explain Giniä, its relevance, and its practical applications in the lives of students, entrepreneurs, and curious individuals. Figure out what noodlemagazine com is all about and why it’s different.
Key Takeaways
- The Gini coefficient is a metric for income inequality that ranges from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (extreme inequality).
- It assists policymakers, businesses, and communities in identifying and addressing glaring income inequalities through targeted interventions.
- Real-world interventions, such as taxation, education, and social programs, can reduce a high Gini score.
- Understanding Gini’s coefficient enables one to analyze economic changes and advocate for equality as a valued principle.
- It can help design effective business and marketing plans, as well as urban social justice interventions.
What Is Giniä, and Why Should You Care?
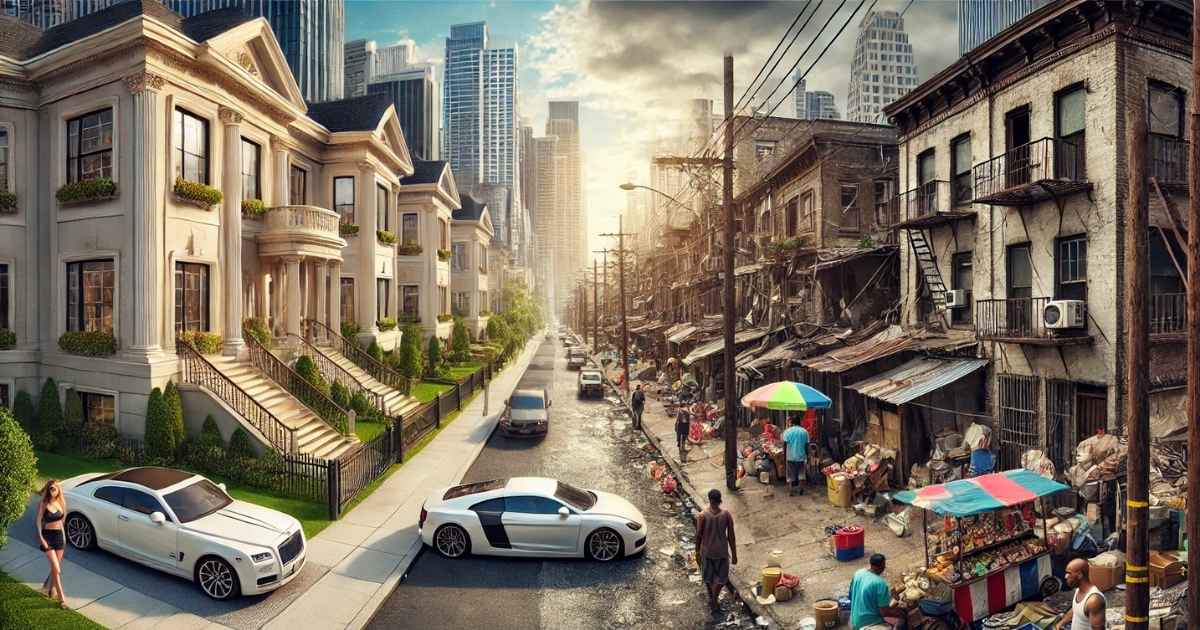
Imagine a family gathering where the cake is distributed so that one cousin takes home 90% and everyone else fights over the remaining scraps. That is the depiction of a high giniä in society. Giniä is short for Gini Coefficient, a term of Italian statistician Corrado Gini. It is a number between 0 and 1 that depicts the evenly spread income within a population. 0 is everyone earning the same, and 1 is one person possessing all the resources. Countries like Sweden and South Africa score 0.3 and 0.6, respectively.
As a college student, a high giniä in your country would mean fewer opportunities for work and education. It can also mean an unstable customer base for your business. It serves as an alert for the community, measuring wealth inequality that hinders progress and triggers violence. Understanding giniä helps in making informed choices by understanding the economy.
How Giniä Is Calculated?
The mathematics associated with giniä may appear daunting, but it is more straightforward than it sounds. Giniā is based on a concept known as the Lorenz curve. The curve measures inequality in income distribution. The further the curve is from the inequality line, the higher the Gini score. No need to worry about the calculations. Economists determine this based on household income data. An example is the World Bank, which collects this data on a global scale and displays trends over time.
Real-World Impacts of Giniä
Imagine if the giniā score were 0.5. This high giniā figure would likely be accompanied by conspicuous wealth inequality. This would mean some people living in the area would drive luxury cars while others would be unable to afford rent. Some of the primary societal impacts include the following:
- Social tension: As inequality increases, weaker segments of society may feel more neglected in comparison to the dominant fraction, leading to protests and higher rates of crime.
- Economic risk: If a significant portion of society is unable to afford products and services, a business’s profitability will be at risk.
- Health and education gaps: People in the lower socioeconomic segment often struggle to afford access to high-quality education and healthcare services.
The giniā score of 0.25 would be a more desirable figure. This would accompany a strong middle class and wider access to opportunities. Denmark is often cited for its high Gini score of 0.25, mainly due to its strong welfare system, which redistributes wealth through taxes and services.
Case Study: Taxes and Giniä
Finland demonstrates the impact of taxation on Gini indices with a Gini coefficient of approximately 0.27. Estimates put its pre-tax score at approximately 0.4. Progressive taxation helps fund free education and healthcare, thereby reducing inequality. In comparison, the United States’ Gini coefficient, hovering around 0.41, is partially a result of less progressive tax policies.
How Giniä Affects You
If you are a student, an entrepreneur, or even a community advocate, the Giniä index affects you practically. Let’s examine this through a few different lenses.
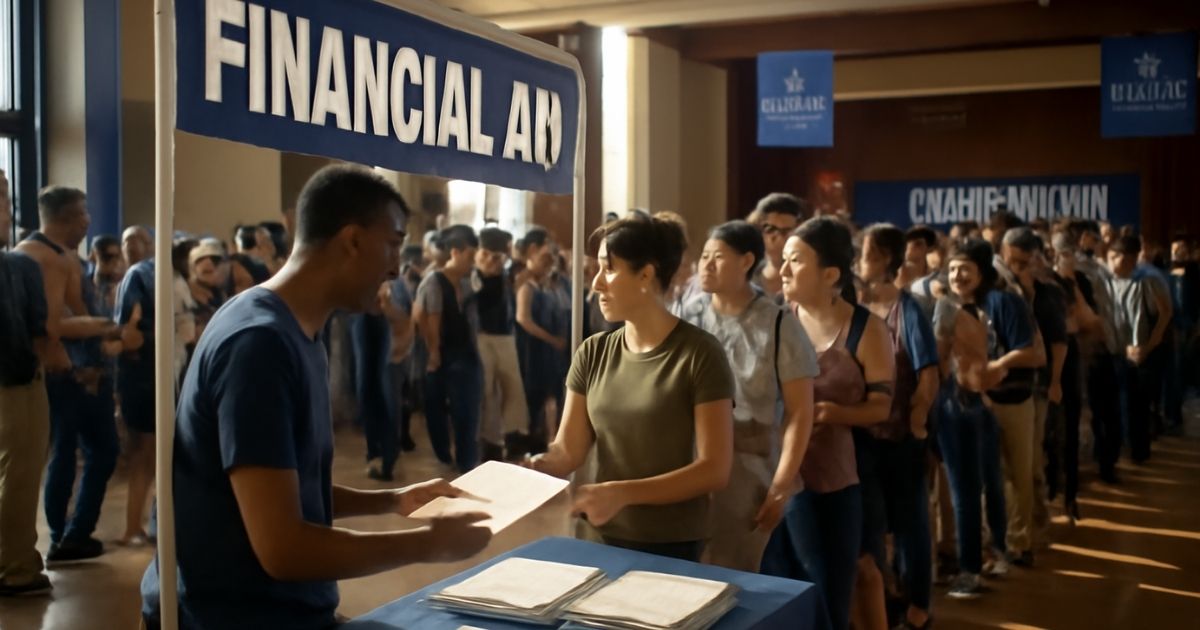
For Students: Education and Opportunity
Graduates, or potential graduates, of higher education institutions face formidable competition to secure places at colleges and universities due to the disproportionate availability. The same is true in ‘public’ education systems: in countries with a pronounced wealth gap, the eastern portion of Brazil, with a Gini coefficient of roughly 0.53, wealthier families grab a disproportionate share. Students in this scenario can leverage an understanding of Giniä to advocate for policies that would allow for the subsidization of tuition or scholarships, thereby alleviating the public burden.
Hack: Look for schemes targeting low-income students. A case in point is the need-based scholarships offered by certain universities, or NGO funded education in high-gini regions.
For Businesses: Market Certainty
It’s your first week operating a new coffee shop. If you’re in a high-Gini city, customer traffic will be limited since not many will be willing to pay for your $5 lattes. Businesses operating in markets with high Gini indices have been shown, in part due to a lack of demand, to have a higher risk of failure. However, with a lower giniä, more people have disposable income, leading to greater business sustainability.
Hack: Focus on giniä to choose your markets. Regions with more equitable income distribution can be identified using the World Bank’s databases.
For Communities: Social Justice
High giniä scores tend to stimulate the most activism. The community groups in South Africa, which has one of the highest giniå scores, use giniä data to advocate for improved housing and wage policies. Understanding giniä indices allows anyone to advocate for more public services or demand tax equity.
Hack: Beat giniä apathy by joining or starting local campaigns that highlight inequality. Arguments based on objective data are much more difficult for decision makers to ignore.
Evaluating Giniä Alongside Other Methods
As with any measure, the Gini coefficient has its own merits and limitations. While it may be beneficial to consider Gini alongside other metrics, the Balanced Development Divide and the Palma Ratio seem to offer the most comparable constructs. The Palma Ratio includes the share of income belonging to the top decile compared to the bottom forty percent. While it is effective, it is overly simplistic and overlooks the upper-middle class.
The Theil index also has its limitations, focusing on inequality among groups that encompass entire regions or races, but it is overly complex and difficult to interpret. Another criticized method is median income, as it only displays the center of the income distribution without taking into account the entire distribution, aiming to measure inequality in the same way as the Gini coefficient does.
Gini remains the winning method due to its inherent qualities and overall reputation as a measure of inequality, providing a snapshot of regional disparities. Other methods might offer deeper insights, but with complex layers of data that feel cumbersome to interpret. Giniä risk oversimplifying the situation, ignoring the plethora of factors that contribute to inequality, including quality of life and access to healthcare, beyond income.
Personal Adjustment Hacks Utilizing Giniä
To help Giniä work for you, the following tips have been compiled to apply to Giniä constructively:
- Research Your Area: Check your country’s Giniä on the World Bank or OECD. Both have extensive databases to shed light on your local economy.
- Critically Engage: Use Giniä in discussions or in campaigns advocating for other policies to be earmarked as free education or progressive tax systems, pushing for change.
- Plan Your Career: Consider relocating to a region with a lower Gini to improve job availability for new grads.
- Business Strategy: Entrepreneurs may want to focus on areas with a Gini score between 0.3 and 0.4, as these represent regions with dependable demand.
- Stay Informed: Monitor Gini for inequalities and forecast economic prospects. For example, increasing Gini could mark an impending economic downturn.
Criticism and Challenges: Focus on the Gini Coefficient and Gini Index
No economic tool is flawless, and Gini is no exception. For one, it only accounts for income, leaving out wealth in the form of properties and savings. Two individuals earning the same income can lead drastically different lives if one is a homeowner and the other a renter. Gini also ignores essential services such as clean water and safety. It is also criticized for lacking a regional focus within a single country.
For instance, India’s Gini coefficient is often estimated at 0.35, but it could be considerably higher in urban areas, such as Mumbai, and lower in rural areas. In any case, Gini remains a preferred metric, as it’s easy to analyze both longitudinally and cross-nationally.
Solving the Gini Index: Implementing Effective Gini Shifts
While there are strategies for improving the Gini coefficient, it is undoubtedly a challenging goal.
- Proposed: Implementing progressive tax policies encourages higher earners to be taxed more to provide public service funding, as seen in Scandinavian countries.
- Education Accessibility: As demonstrated in Finland, free or affordable schools promote equity among students.
- Social Programs: Welfare, along with healthcare and housing, provides additional services to support those in lower-income brackets. Canada exemplifies this with a Gini index of approximately 0.32.
- Job Creation: Policies that foster small businesses or technology sectors promote equitable income distribution, as observed in Germany.
A 2019 report by OECD demonstrated a direct correlation between social welfare services and lower Gini index scores. Countries with strong social safety nets have Gini scores 10-20% lower than those without.
Gini in Action: A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine, for a moment, that you are a city planner in a city with a Gini index of 0.45. You observe that poorer neighborhoods often lack public parks and quality schools, while wealthier neighborhoods tend to thrive. With the Gini data in hand, you propose a budget that includes higher taxes for the public sector, which services and funds the construction of schools and parks in poorer neighborhoods. Over five years, the public works and employment initiatives that are built result in a reduction of the Gini to 0.38. The residents feel a boost in community, and local businesses thrive as their services are used more often by additional customers.
Change starts with understanding the Gini index, and Gini data informs decision-making.
Why Giniä Matters Today
Today, in the year 2025, the ongoing geopolitical events, pandemics, and economic shifts continue to be a hot topic of discussion as they have widened the gaps of inequality in many countries. An example of this is that the World Bank noted a spike in inequality in developing nations in 2022, as of this date, due to job losses. Knowing giniä scores enables you to stay ahead of the trends regardless of whether you are planning to start a business, vote for a policy, or simply prepare for the future.
Conclusion: Giniä Enables You to Act
Ginad is not just a number; it portrays the fairness of the society. Averaging society’s Gini score indicates the wise choices to be made, ranging from career choices to advocating for and acting on changes. You can begin by searching for your country’s Gini score. From there, you can start wondering how it impacts your daily life and personal decisions. If you are hoping to have a positive impact, support targeted education and job creation policies. These small changes can have a significant effect. To create positive impacts, the first few steps can include finding a local advocacy group to support and begin building a transformative effect on your local market for your business.